Quick Leads
Flexible PCB Disadvantages: Key Limitations for Engineers and Designers
Flexible printed circuit boards (PCBs) have become popular in the electronics industry because they’re lightweight, save space, and can be shaped to fit into unconventional designs. But, despite these advantages, flexible circuits have some disadvantages. If you’re an engineer, product designer, or decision-maker, you need to know about these downsides so you can decide if flexible PCBs are right for your application.
In this article, we’ll explore the key disadvantages of flexible PCBs, including high costs, durability concerns, size limitations, and complex manufacturing requirements.

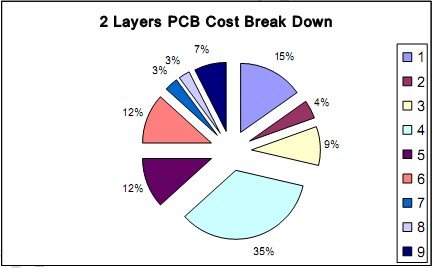
High Initial Cost
One of the biggest disadvantages of flexible PCBs is that they’re expensive. Unlike rigid PCBs, which often follow standardized designs, flexible circuits have to be custom designed and prototyped for your specific application. This customization means you have to pay higher one-time costs for:
- Special materials, like flexible substrates.
- Extra steps in the design phase, like figuring out where the flex points will be.
- Custom tooling and manufacturing equipment.
If you’re only making a few boards, these costs can easily outweigh the benefits, making flexible PCBs a less viable option for projects with tight budgets. You have to decide if the long-term advantages of flexible PCBs are worth the upfront cost.
Durability Issues with Flexible Circuits
While flexible PCBs are made to bend and flex, they’re more susceptible to environmental factors and physical stress than rigid PCBs. Some of the things that can affect the durability of flexible PCBs include:
- Heat and moisture: Flexible materials are more susceptible to environmental stress, especially in extreme conditions.
- Cracking under stress:If you bend or move them too much, the conductive traces can crack.
- Hard to fix once they’re broken: Unlike rigid PCBs, flexible circuits are harder to repair, and damage often results in complete failure.
Here’s an example: In industrial applications where equipment is exposed to frequent temperature changes or vibrations, flexible PCBs might not last as long as rigid boards, so you’ll have to replace them more often.
Size and Manufacturing Limitations
While flexible PCBs are great for small, lightweight applications, they do have size limitations. You can only make them so long, which can limit the designs you can do if you need a big or complex circuit.
Rigid PCBs, on the other hand, can be made bigger and offer more structural integrity for complex systems. That’s why flexible PCBs aren’t great for applications where you need a really long circuit or a really big one.
Why the size matters:
- Small, flexible designs are perfect for wearable tech and small devices, but they’re not good for big industrial systems.
The size limitation can be a big problem if you’re a product developer working on a big, multi-layer board or a big board.

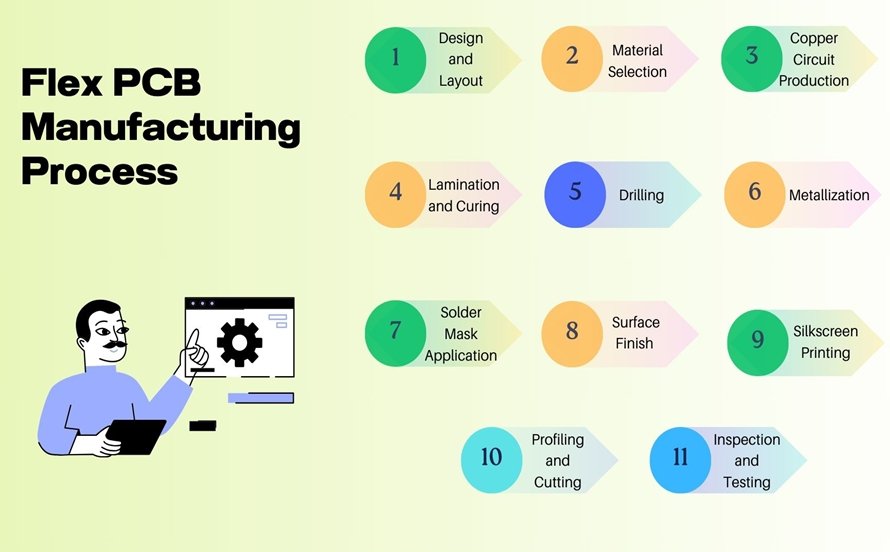
Complex Manufacturing Process
The process of manufacturing flexible PCBs is more intricate and involves several unique steps, which add to both the time and cost of production. Here’s why:
- Specialized equipment is required to handle the delicate materials used in flexible circuits.
- Precise manufacturing steps are necessary to ensure the PCB can bend without causing damage, including controlled flexing during production.
- Protective coatings or adhesives may need to be applied to improve durability and prevent damage during handling or installation.
Making flexible PCBs is more complicated and has more steps, which takes more time and costs more money. Here’s why:
- You need special equipment to handle the delicate materials used in flexible circuits.
- You have to follow precise manufacturing steps to make sure the PCB can bend without breaking, including controlled bending during production.
- You might have to put a protective coating or adhesive on the board to make it last longer and keep it from getting damaged when you handle it or put it in your product.
Because of all these extra steps, it takes longer and costs more to make flexible PCBs, especially if you’re only making a few boards. If you’re working on a tight deadline, the extra steps can slow you down, so you might not want to use flexible PCBs.
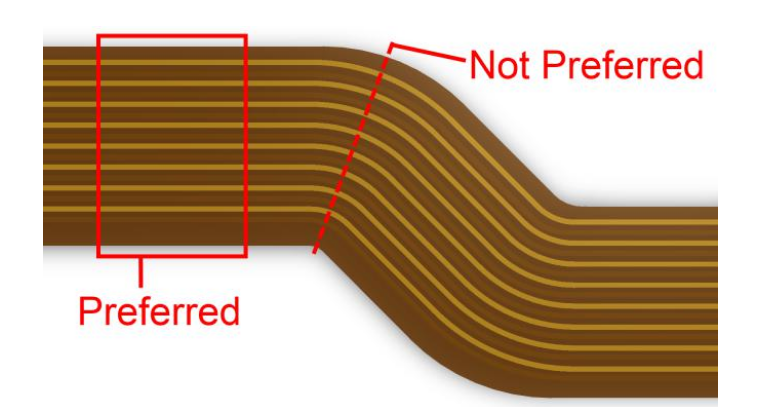
Prone to Damage from Improper Handling
Flexible PCBs are made to bend, but they’re delicate and can get damaged when you put them together or put them in your product. If you don’t handle them right, you can break the conductive traces, which can make them not work or stop working sooner than they should.
Specific risks include:
- Bending them too much or putting too much pressure on them when you put them in your product.
- Not handling them right when you put them together.
- Stuff in the environment, like dust or static electricity, can mess them up when you make them.
Here’s an example: In wearable tech, where you bend flexible PCBs over and over again, if you don’t handle them right when you put them together, you can crack the circuit, and then the whole thing doesn’t work.
Electrical Performance and Handling Issues
Flexible PCBs don’t work as well as rigid PCBs because they’re made with thinner, more flexible materials. They don’t handle electricity as well, especially if you’re using a lot of power. That’s why they’re not great for applications where:
- You need a lot of power.
- You’re using parts that need a lot of power.
For example, in big industrial equipment that uses a lot of power, rigid PCBs might be better because they can handle more power without messing up the circuit.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Are flexible PCBs more expensive than rigid PCBs?
Yes, flex PCBs usually cost more upfront because they’re custom designed, made with special materials, and require complicated manufacturing processes.
Q: What applications are flexible PCBs not suitable for?
Flex PCBs aren’t as good for high-power applications, big designs, or places with lots of heat, moisture, or mechanical stress.
Q: What environmental conditions affect flexible PCB durability?
Flex PCBs can be damaged by heat, moisture, chemicals, and bending them too much. These things can make them stop working and die faster.
Special Offer: Get $50 off your order!
Please email sales@unitcircuits.com for details.
Conclusion
Even though flex PCBs are great for small, light designs, they’re expensive, not very tough, can’t be made too big, and are hard to make. That makes them not as good for some things. You have to think about all that before you decide to use them.
If you’re not sure whether to use flex or rigid PCBs for your next project, get in touch with us at sales@unitcircuits.com. We’ll help you figure it out and give you a fast, accurate price. It doesn’t matter if you’re making consumer electronics, industrial systems, or something else. We can help you.
Find out why flexible PCBs are expensive, not very tough, and hard to make. Learn when you shouldn’t use them.

